Anderson-Darling Test for Normality
The Anderson-Darling Test for Normality is a distance or EDF (empirical distribution function) test. It is based upon the concept that when given a hypothesized underlying distribution, the data can be transformed to a uniform distribution. The transformed sample data can be then tested for uniformity with a distance test (Shapiro 1980).
In comparisons of power, Stephens (1974) found A2 to be one of the best EDF statistics for detecting most departures from normality. The only statistic close was the W2 (Shapiro-Wilk Test) statistic.
Procedure
- The data is sorted from low to high.
- The Mean,
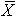 , and Standard Deviation, s, are calculated.
, and Standard Deviation, s, are calculated. - The values are standardized using:
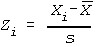
- Pi is calculated using the significance of Zi; where Pi is the upper tail p-value of Zi.
- A2 is calculated using:
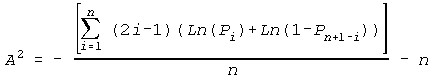
- A2*, an approximate adjustment for sample size, is calculated using:
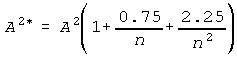
Note:
If s=0 or any Pi=(0 or 1) then A2 cannot be calculated and is undefined.