A Binomial Distribution is a discrete Random Sampling Distribution. The sampling is from a series of n independent trials each of which may have outcomes which fall into one of two classifications. The probability of occurrence of each classification remains constant for each trial. The outcomes of each successive trial also remains independent. This sampling situation is sometimes referred to as a Bernoulli Trial or Process.
Calculations
The probability of exactly r occurrences in n trails may be calculated by the following Binomial formula.
![]()
Where:
- r is the number of occurrences,
- n is the sample size, and
 is the probability of occurrence.
is the probability of occurrence.
Other Properties
The Binomial Distribution may be approximated with a Normal Distribution with a Mean and a standard deviation as follows.
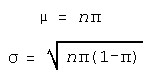
The limit of the Binomial Distribution, as n goes toward infinity, and p goes toward zero, yields a Poisson Distribution, with ![]() equal to np.
equal to np.
example
Here is an example Binomial Distribution, assuming a sample size of 10, and a probability of occurrence of 0.2. The probability of 5 or more occurrences in a sample of size 10, with a probability of occurrence of 0.2, is 0.0328.
Binomial Distribution
p = 0.2000 n = 10 np = 2.000
Prob Equal & Equal &
r at r Above Below
0 0.1074 1.0000 0.1074 |------------
1 0.2684 0.8926 0.3758 |-------------------------------
2 0.3020 0.6242 0.6778 |-----------------------------------
3 0.2013 0.3222 0.8791 |-----------------------
4 0.0881 0.1209 0.9672 |----------
5 0.0264 0.0328 0.9936 |---
6 0.0055 0.0064 0.9991 |-
7 0.0008 0.0009 0.9999 |
8 0.0001 0.0001 1.0000 |
9 0.0000 0.0000 1.0000 |
10 0.0000 0.0000 1.0000 |