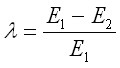Correlation - Interval Level Data
Pearson Product Moment Correlation Coefficient
The Pearson Product Moment Correlation coefficient is a measure of correlation between two variables measured on an interval level scale or higher. It measures the strength of a linear relationship between the two variables.
![]() is known as the "Coefficient of Determination." This measures the proportion of variance in Y that can be explained by the variation in X, given a linear relationship with X.
is known as the "Coefficient of Determination." This measures the proportion of variance in Y that can be explained by the variation in X, given a linear relationship with X.
The Pearson Product Moment Correlation may be calculated as follows.
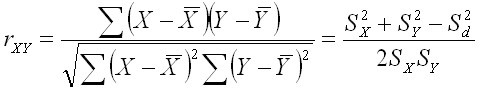
Correlation - Ordinal Level Data
Spearman Product Moment Correlation Coefficient
The Spearman rank-order correlation coefficient, r(s), is a measure of association between two variables measured on at least an ordinal scale. The Spearman correlation coefficient may be used in place of the Pearson correlation for interval data when questions arise concerning the underlying assumptions.
The correlation coefficient is generated by separately ranking two dependent variables and then calculating the standard Pearson correlation on the ranks. The significance may be evaluated with the standard Pearson significance test. An exact table is below for small sample sizes.
| n | Critical r(s) |
|---|---|
| 5 | 1.000 |
| 6 | 0.886 |
| 7 | 0.786 |
| 8 | 0.738 |
| 9 | 0.700 |
| 10 | 0.648 |
| 11 | 0.618 |
| 12 | 0.587 |
| 13 | 0.560 |
| 14 | 0.538 |
| 15 | 0.521 |
| 16 | 0.503 |
| 17 | 0.485 |
| 18 | 0.472 |
| 19 | 0.460 |
| 20 | 0.447 |
Correlation - Nominal Level Data
Point Biserial - Two-level Nominal with Interval Level variables
The Point Biserial is used with a two-level nominal level variable and an interval level or higher variable. The Point Biserial is calculated using the formula for the Pearson Product Moment Correlation Coefficient.
Chi-Square Statistic - Nominal Level Variables
The Chi-square statistic is used to test for independence between the rows and columns of a table of frequencies. The statistic is calculated as follows.
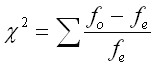
This statistic is distributed according to a Chi-square distribution with (R-1)(C-1) degrees of freedom.
Phi - Cramer's V - Nominal Level Variables
Phi is for 2 x 2 tables only. Cramer's V is for higher level tables. These statistics are chi-square-based measures. Phi is calculated as follows.
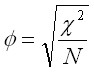
Cramer's V is calculated as follows.
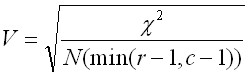
Lambda - Nominal Level Variables
Lambda is a "proportional reduction in error" (PRE) measure of association. For nominal level variables, PRE involves predicting which category each case will fall on the dependent variable (Y), while ignoring the independent variable (X). Then a prediction is made again taking into account the independent variable. If the variables are associated, the information provided by the independent variable should reduce the errors of prediction. The stronger the association, the lower the error rate will be.
Let E1 be the prediction errors made while ignoring the independent variable, and E2 be the prediction errors made while taking the independent variable into account. Lambda is then calculated as follows.