Performance Analysis for Process Improvement

Originally appeared in ASQ’s 52nd Annual
Quality Congress Proceedings, May 1998
Michael V. Petrovich
MVP Programs
SUMMARY
Process performance analysis, introduced here, uses performance measures such as Pp, Ppk, and Ppm with analysis to assess performance, sources of variation, process potential, and improvement opportunity. This analysis may be conducted where control may not have been achieved and where a large number of process streams exist.
KEY WORDS
performance measures, Ppk, Ppm
INTRODUCTION
The quality goals of an organization include the elimination of nonconformance and the minimization of variation around appropriate targets. The quality practitioner needs to know how well these goals are being realized. Specifically, one must ask, “How well are my processes performing and what must I do to improve?”
For many years process assessment has employed the use of process capability measures. These include Cp, Cpk, and more recently, Cpm. For a review of these see Rodriguez (1992). The use of these measures requires demonstration of statistical control followed by a distribution assessment compared against the targets and specifications. Difficulties arise when statistical control cannot be assumed and also where a large number of process streams may be present. Here are a few examples.
- A plastic lid manufacturer has 40 molding machines, 54 tools per molder. Tools are replaced every few weeks, and tool-to-tool differences are found. In addition, slight differences are found as batches of raw materials are changed. Other sources of variation include maintenance cycles, startup periods, and any possible adjustments made by the operating personnel.
- A metal bottlecap company has eight presses, each containing 22 dies. Slight differences exist die-to-die and press-to-press. In addition, the process exhibits tool wear and slight fluctuations are observed with lot-to-lot changes in steel.
- An aluminum can manufacturer has two lines in one of its plants. Each line contains 16 stations. Stationto- station differences are found. This process also undergoes tool wear and perfect through-time stability (or control) is not observed in many of the stations.
Traditional capability assessments are inadequate to handle these situations. If control cannot be demonstrated, traditional assessments of process capability cannot be properly made. In addition, the presence of a large number of process streams would yield a combination of distributions that would present a nightmare to mathematically model. In the meantime, quality practitioners still need a means of assessing their processes and the effectiveness of their improvement strategies.
In recent years process performance measures have gained popularity. These measures, introduced by Herman (1989), are analogous to their counterpart capability measures. A “P” representing “performance” replaces the “C” found in “capability” indices. The most popular performance measures are Pp, Ppk, and Ppm. These measures may be used to answer questions concerning how well the process is performing and may be employed before a process is documented to be in a state of statistical control.
As introduced here, process performance analysis utilizes performance measures and graphical techniques to display performance, potential performance, and to determine the sources of quality losses. process performance analysis provides a means to
- Assess processes before statistical control is achieved
- Determine sources of process loss
- Make comparisons among characteristics, products, plants, and suppliers
- Determine control and improvement priorities
- Assess the results of process improvement efforts
SAMPLING
To study processes, samples must be taken and measurements made for critical characteristics. The approach suggested here is to measure total outgoing variation as sent to the customer. Total outgoing variation results from variation inherent to the process as well as variation from lot-to-lot, tool-to-tool, line-to-line, shift-to-shift, setup-tosetup, day-to-day, and throughout maintenance cycles. Sampling will generally be done at end-of-line. To provide diagnostic capability, stratified sampling by lines, tools, or other process streams may also be desired.
To assess the performance of a process, and to reflect the total outgoing variation, long periods of data collection with large data sets are preferred. A minimum of one month, and more preferably three months, worth of data is desired. While the analysis may be done with a few hundred data values, 1000 is a desired minimum; 10,000 or more values may be used to provide better analysis. If 100 values were obtained each day, 9000 values would be accumulated during a calendar quarter.
Of course, an appropriate measurement system analysis should be conducted prior to data collection. This analysis should assess both the stability of the measurement system as well as the variance contributed by measurement error. The methodology for conducting this type of analysis may be found in numerous texts. See, for example, Chrysler, Ford, and General Motors (1995).
PROCESS PERFORMANCE MEASURES
Process performance measures provide an assessment of processes in which process control may not have been achieved. These measures take into account all observed variation from both common and special causes, whereas traditional process capability measures consider only the inherent, common cause process variation.
Performance measures assess the historical performance of a process. Any prediction from them would be useful only to the extent that the future is expected to resemble the past. To capture total variability in a process, performance measures should be assessed from data collected over long periods of time.
When a process is not in a state of control the process distribution is changing through time. Hence, attempts to determine a specific form of a process distribution would be inappropriate. For this reason, performance measures should not consider distributional shape.
Several measures of process performance may be calculated. In this discussion, Ppm, Ppk, and Pp will be shown. Another measure, Pp(process stream), will be used to examine the performance within a process stream. Finally, a potential measure, Cp, will be estimated. Cp may be used to assess the potential of the process. Making comparisons among these measures will highlight process losses and improvement opportunities.
Taguchi (1986) defined a loss function which quantifies the losses due to manufacturing variation. As product characteristics depart from their design target, this loss function states that the loss will be proportional to the target deviation squared. Chan, et al. (1988) created a capability measure, Cpm, which is inversely related to this loss.
The first performance measure discussed here, Ppm, is derived from Cpm and is inversely related to the losses in a manufacturing process. The higher the Ppm value, the better the process performance. When a target, upper, and lower specification are given, Ppm may be calculated by
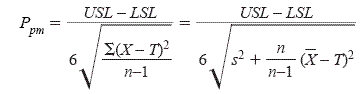
where
USL is the Upper Specification Limit
LSL is the Lower Specification Limit
X is the observed value
T is the Target
s2 is the sample variance from all combined data
X-bar is the sample mean from all combined data,
and n is the total number of observations
For a single specification and target the following may be used
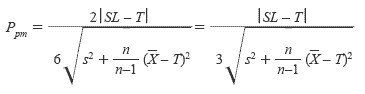
where SL is the Specification Limit.
The use of Ppm assumes valid specifications and targets are given and representative samples are generated during the period of interest. When appropriately employed, Ppm may be used as a primary measure to assess the performance of a process. Process performance will improve, as measured by increases in Ppm, as the process is brought into better control; systematic variation such as differences in tooling, setup, operators, machines, and materials is reduced; and the process is brought on target. Ppk is recommended when no target is given.
Ppk may be calculated as follows.
Pp is another performance measure which assesses variation but not location. Pp is calculated as follows.
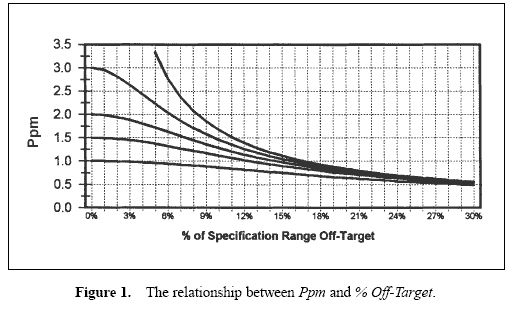
The difference between Ppm and Pp is the term which includes the deviation from target. If the observed process average was on target, Ppm and Pp would be identical. Calculation of Pp and making comparisons to Ppm will yield an understanding of the loss from being off target. An additional diagnostic measure, % Off-Target, may also be calculated. This measure represents the percent of the specification range the mean falls from target.
As the process average departs from target, Ppm is reduced. Figure 1 graphically displays the relationship between Ppm and % Off-Target. The resulting Ppm is shown for four levels of Pp (at infinity, 3, 2, 1.5, 1) as the offset from target varies. The highest line represents a process with a standard deviation of zero (Pp at infinity). If a process is running with a mean 10 percent off target, the largest Ppm that may be achieved is 1.67. At 30 percent off target, the largest Ppm that may be achieved is 0.56.
If the process under study contains multiple lines, tools, or stations (process streams), the losses from differences between these process streams should be understood. Pp(process stream) is a measure of the process performance within process streams. If no process stream differences exist, and the process is on target, Ppm would be equal to Pp(process stream). Pp(process stream) may be calculated by
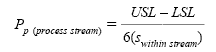
where swithin stream is the square root of the average of the variances within each process stream calculated by
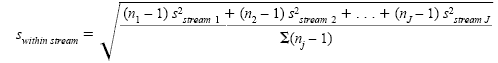
where J is the number of process streams.
A useful diagnostic measure is the percent process stream difference. This measure is simply the range of the process stream means divided by the specification range expressed as a percentage.
Another important diagnostic assessment concerns the losses which arise from a lack of through-time stability or control. The swithin stream includes any sources of through-time variability. The question to answer is, “If perfect through-time stability were achieved, how much variation would be observed?” To address this question, the minimum potential process variation, spotential, may be estimated. Several approaches may be used for this estimation. Two common approaches are
- Short-term capability studies
- Estimating variance within process streams using average or median dispersion statistics
Short-term capability studies may be conducted to determine the inherent potential variation of the process. This may be done by generating one or more studies of relatively small samples of consecutive items and then estimating the potential variability. Preferably, multiple studies should be conducted at different points in time.
Several approaches to estimate the potential variation may be employed when using data sampled over an extended period of time and where control may not be observed. One common approach is to remove individual outof- control points and to estimate process variation from those points remaining. Unfortunately, this methodology is not feasible with large data sets.
Another approach to estimate the potential variation is to use averages or medians of dispersion statistics such as the range, moving range, or standard deviation. These average or median statistics may be used to generate an estimated s by dividing by appropriate constants. [See Wheeler (1995) for tables of constants and methods of calculation.] Median dispersion statistics are more robust to significant shifts in the process than average dispersion statistics. Although there is more sampling error associated with median dispersion statistics, this is not an issue with a large number of samples.
The potential variation includes measurement error. If desired, measurement error variance may be subtracted from this estimate to assess the true product variation (σ2 product = σ2potential – σ2measurement ). This may be a concern if large measurement error variance exists (Herman 1989).
The rate of sampling may influence the estimated potential variation. When using statistics which assess item-to-item variation, shorter time intervals between sampled items would generate lower estimates of potential variance. Sampling consecutive items would result in minimum estimates.
When multiple process streams are present, estimate the potential variation for each process stream. In these cases, use the average of the estimated standard deviations for estimating process potential, assuming potential variances are equal among process streams. If large differences exist in variation, separate analysis for each process stream may be desired.
Using the estimated potential variation, spotential, a measure of the potential capability of the process, Cp(potential), may be calculated as follows.
This potential capability is the potential performance measure (Ppm) that would be obtained if the process were brought into control, process stream variation was eliminated, and the process was brought on target.
OBSERVED NONCONFORMING RATES
Since distributional analysis is not done with performance measures, and through-time stability may not be achieved, the use of process performance measures should be accompanied with examining the actual observed nonconforming proportion. Using the total number of items examined and the number outside the specification limits the nonconforming proportion may be calculated. Translating the total nonconforming to parts per million (ppm) may be useful.
PROCESS PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
The following relationships will hold when generating performance measures.
A stacked bar chart may be used to display these relationships. Using the performance measure Ppm as a base, stacked bar charts may be created by using sections which represent the incremental differences between the performance measures. The height of each section displays the various performance measures. These bar charts show the observed performance and the improvement potential if the process is brought on target, the process stream variation is removed, and the process is brought into control. An example is shown in Figure 2. These bar charts represent data from two plants manufacturing aluminum cans.
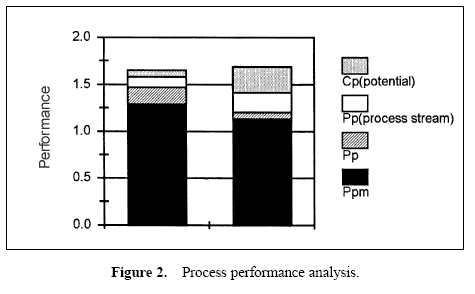
The sections of the bars in the chart show the potential performance improvement that would occur in the Ppm value when various improvements are made.
- The lowest section of the bars show the observed performance measure, Ppm.
- The top of the second section of the bars show the performance had the process average been on target.
- The top of the third section of the bars show the performance of the process had the means for each process stream been on target.
- The top of the highest bar sections show the potential of the process if through-time variation is removed (control achieved) and each process stream mean is on target.
While the areas of the top three bar sections can be thought of as observed losses, these areas cannot be compared. The improvement potential seen on the stacked bar chart occurs when the process is brought on target, then process stream differences are removed, and finally through-time stability is achieved. Note that changes in higher bars represent a smaller change in process variation than a change in a lower bar.
The total variance about target, τ2, can be decomposed into the various components that can be compared to assess improvement priority.
These components may be approximated as follows and displayed in a pie, bar, or Pareto chart.
σ2potential may be estimated as described previously and may also be decomposed into σ2product and σ2measurement, as described earlier.
σ2off-target may be simply estimated as follows.
The variance from process stream differences may be estimated many ways. If the data have not been stratified, studies may be conducted to determine the variance contribution from process stream differences. These studies may include all streams of interest or a random selection of streams. Methods such as analysis of variance (ANOVA) may be used to estimate this component. Remember though, that the process is not assumed to be stable and these assessments should be considered approximate. If the data have been stratified by all process streams of interest, the process stream variance may be simply estimated as follows.
where, again, s2 is the sample variance from all combined data. The variance from through-time process changes, σ2time, may be estimated as follows.
![]()
EXAMPLE
Aluminum lids are produced on a machine with 22 stations. Each day, lids from each station are sampled and the lid height is measured. Data are collected over a three-month period. The specifications for this characteristic are 98 ± 5. Table 1 provides an analysis of these data.
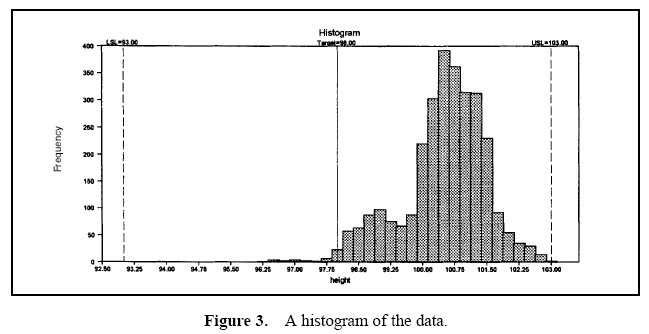
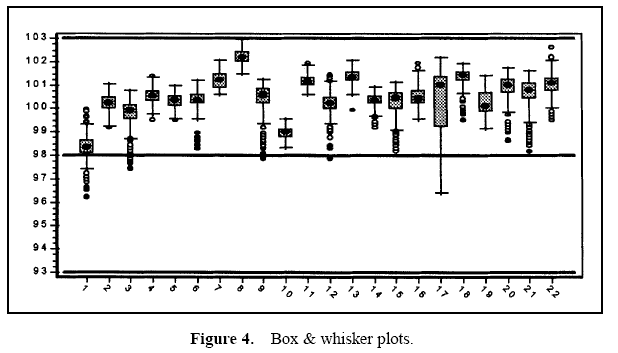
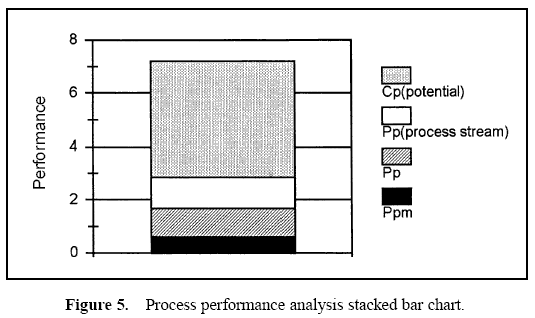
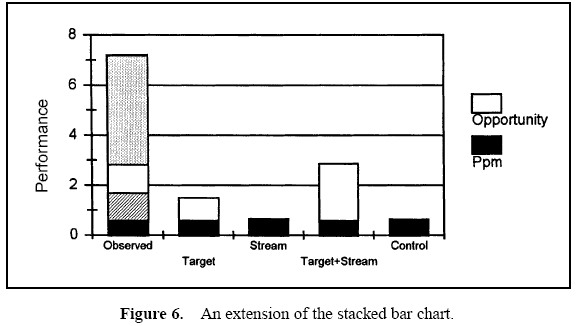
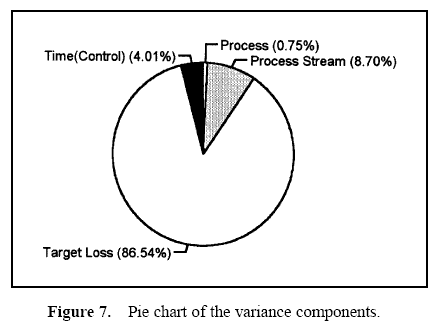
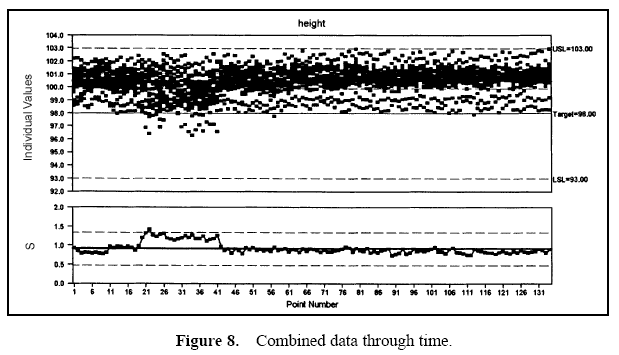
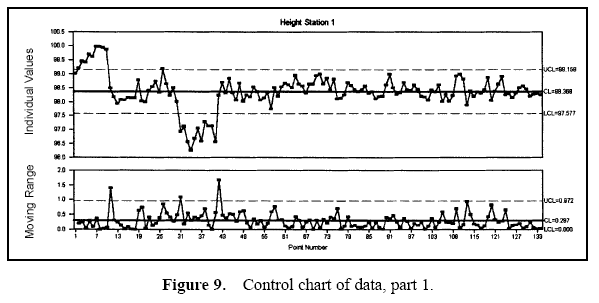
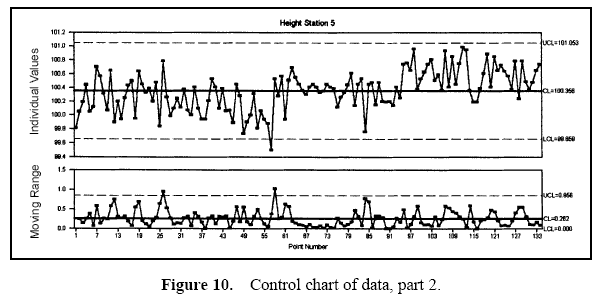
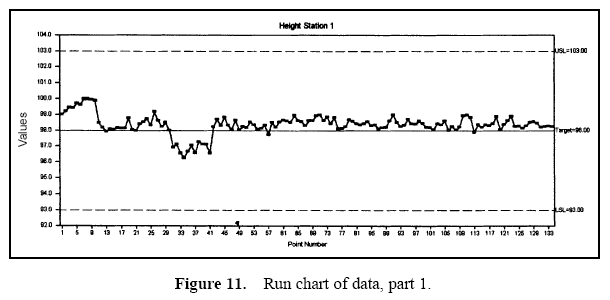
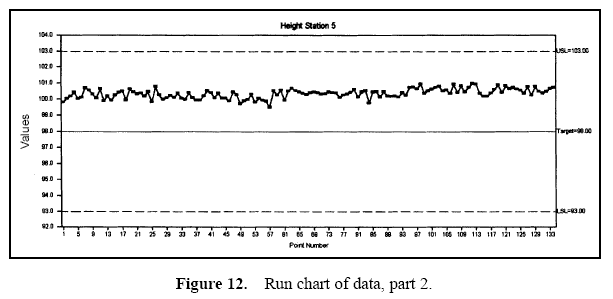
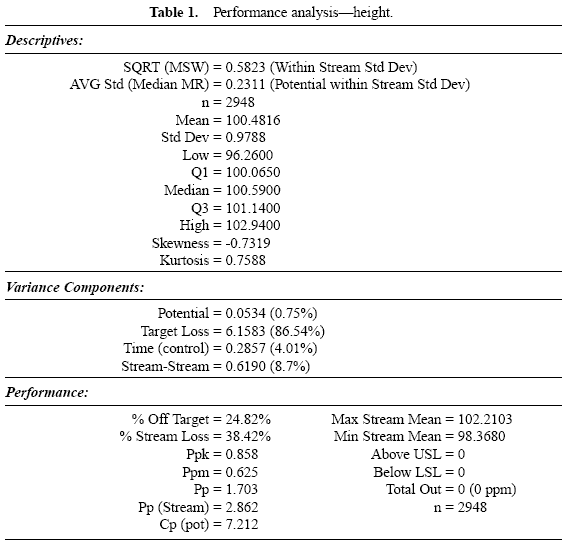
Table 1 displays the descriptive measures, the variance components, and the performance calculations. Figure 3 displays a histogram of all the data. Figure 4 displays box and whisker plots for each of the 22 stations with the target and specifications. Figure 5 displays a process performance analysis stacked bar chart. Figure 6 shows an extension of the stacked bar chart. Figure 6 shows the original stacked bar chart plus the effects on performance for various improvements. The second bar height shows the performance if brought on target, the third shows the performance if the process stream differences were removed, the fourth shows both the target and stream effects removed, and the fifth shows the effect if the through-time instability was removed.
Figure 7 displays a pie chart of the variance components. Figure 8 shows the combined data through time. Figures 9 and 10 show control charts for two stations. The same data from these stations are displayed in Figures 11 and 12 on a run chart with the specifications drawn.
From these charts, it can be seen that the biggest opportunity comes from getting the individual stations on target. While improvement in control will minimize variation, the through-time sources of variability do not represent the largest opportunity. Measurement error analysis is not shown, but from the process potential assessment, measurement error may be considered negligible.
These results are typical of many observed processes. Improvements in targeting and reduction of stream-tostream differences often represent an important opportunity. While improvement in through-time stability or control does not represent a large improvement opportunity in this case, it may be critical in others.
CONCLUSION
The use of process performance measures generated with data collected over extended periods, combined with performance analysis which decomposes sources of variation, provides quality practitioners the ability to answer questions about how their processes are performing and what opportunities exist for improvement. The graphical display of these measures allows one to view the improvement potential. This display may be used to compare multiple processes and characteristics and assist in improvement prioritization. Performance measures such as the Ppm may be used to validate improvement efforts. If through-time stability is improved, tooling or station differences are minimized, and the process is brought on target, Ppm will display an improvement.
REFERENCES
Chrysler Corporation, Ford Motor Company, General Motors Corporation. 1995. Measurement Systems Analysis. Southfield, MI: Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG).
Herman, John T. 1989. Capability Index—Enough for Process Industries? 1989—ASQC Quality Congress Transactions. 92–104.
Rodriguez, Robert N. 1992. Recent Developments in Process Capability Analysis. Journal of Quality Technology, Vol. 24, No. 4, 176–187.
Chan, Lai K., Cheng, Smiley W., and Spiring, Frederick A. 1988. A New Measures of Process Capability: Cpm, Journal of Quality Technology, Vol.20, No. 3, 162–175.
Taguchi, G. 1986. Introduction to Quality Engineering. Tokyo, Japan: Asian Productivity Organization.
Wheeler, Donald J. 1995. Advanced Topics in Statistical Process Control. Knoxville, TN: SPC Press.